Defensible detection-tuning with Kibana Cases: a DFIR how-to
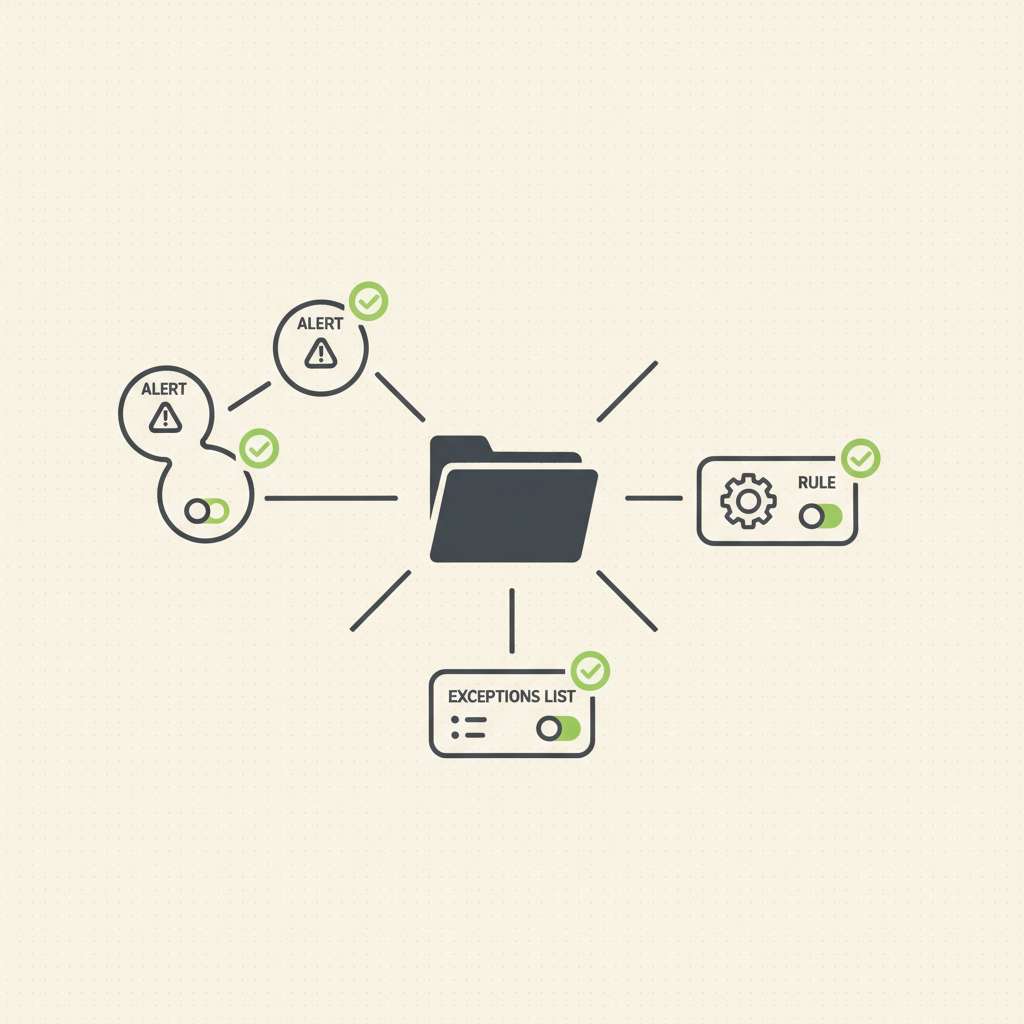
Elastic Security Labs published a workflow on December 5, 2025 that shows how to automate detection-tuning requests with Kibana Cases, using custom fields, a detection to watch for toggled requests, and a webhook to create tickets and add links back to the case (Elastic Security Labs, 2025-12-05).
Overview
Kibana Cases lets you open, track, and enrich investigations with alerts, comments, files, visualizations, and external tickets via connectors such as ServiceNow, Jira, Slack, and webhooks (Cases overview, connector catalog). Custom fields for Cases (text/toggle) were added in Elastic 8.15, enabling standardized “tuning requested?” switches captured directly in the case form (custom fields in settings, Security app settings). You can attach alerts to cases from the Alerts UI or create a case from an alert, ensuring the detection context travels with the request (create/manage cases and attach alerts).

